
A bidirectional relationship between schizophrenia and epilepsy emerged from an analysis of a health insurance database . . .

A bidirectional relationship between schizophrenia and epilepsy emerged from an analysis of a health insurance database . . .

Depression, anxiety, and delirium are 3 examples of common but frequently challenging areas of distress in pediatric palliative care patients.

The articles in this Special Report reinforce the lesson that children come with parents. This is one of first lessons that I teach my residents: you can’t work with a kid in a vacuum. Parents who do not feel some connection with a caregiver will not bring their child to treatment or follow the recommendations of the treatment team.

This column has always been about the world of molecular mental health research. I revisit the technology in this column, now aimed at one of molecular neuropsychiatry’s most intractable, frustrating lines of research: the molecular/cellular basis of schizophrenia.

What follows is an excerpt from Dr Knoll’s introduction to his series Tales From the New Asylum, several of which are posted on his blog.

On the wide range of symptoms in schizophrenia, including alterations of the dopaminergic and/or glutamatergic systems, abnormal neurodevelopment, and the theory of immune system imbalance.

An initiative from the BRIDGE study group has determined that approximately half of patients presenting with a depressive episode are mistakenly diagnosed with unipolar major depression.

blog title

I don’t like to use the worn out word . . . “bruise” in my poems, but this morning . . . one appears on my inner thigh

Several available agents in addition to methylene blue are being investigated for bipolar disorder and were in a in a recent review.

A New Study Looks at What Works-And What Doesn’t

Depression, PTSD, panic disorder, and abuse of alcohol and drugs are more insidious, quieter forms of illness that can cause the same desperation and disability as psychotic disorders.

A study presented by Canadian investigators at the 24th Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology (ECNP) in Paris, September 5 evaluated whether methylene blue can reduce residual symptoms of depression and mania in bipolar disorder.

“The e-mail earnings . . . the enduring, rewarding relationships you’ve always wanted . . . a higher sense of purpose and life satisfaction . . . less stress . . . overall happiness.” All this in just 2 convenient 50-minute sessions!

What is associated with increased suicidal risk in soldiers? In what group is the incidence of postpartum depression highest? These questions and more in this quiz.

Are antidepressants active placebos or lifesavers? Are they overprescribed? Are clinical trials of these drugs insufficient?

Mental health reform is one of the world’s “grand challenges.” Mental, neurological and substance-use (MNS) disorders constitute 13% of the global burden of disease, surpassing both cardiovascular disease and cancer.

In preparing DSM-IV, we worked hard to avoid causing confusion in forensic settings. Realizing that lawyers read documents in their own special way, we had a panel of forensic psychiatrists go over every word to reduce the risks that DSM IV could be misused in the courts.

The first week in October. Leaves fall. Kids start school. Temperatures descend. Weather fluctuates. Stigma decreases. Awareness rises-with the help of the 21st anniversary of NAMI's Mental Illness Awareness Week.


PT blogger

PT Blogger

PT Blogger Bio

The DSM-5 attempt to “dimensionalize” the diagnosis of personality disorder has worthy goals, but has suffered from grievously incompetent implementation.
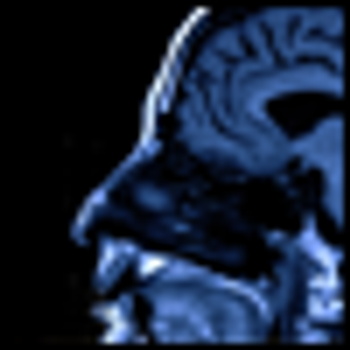
A meta-analysis of depression and risk of stroke finds a positive association. How will this information affect your practice?

Eghigian, Pols, Killen

When it comes to e-mail, I typically warn my [physician] clients of the following.

Knoll, Pies, Moffic, Blumenfield

Andreas Killen, PhD, is Associate Professor of History at the City College of New York and the CUNY Graduate Center. He has held fellowships at the UCLA Humanities Consortium and the Max Planck Institute for the History of Science. Among his publications are Berlin Electropolis: Shock, Nerves, and German Modernity (University of California Press 2006) and a special volume of Osiris that he co-edited on the history of the human sciences. Currently he is working on a book about the relation between film and the human sciences in early 20th century Germany.
