
The steadily rising rate of suicide in the US is a vexing public health crisis. Among the many risk factors for suicidal thoughts and behaviors is sleep disturbance.


The steadily rising rate of suicide in the US is a vexing public health crisis. Among the many risk factors for suicidal thoughts and behaviors is sleep disturbance.

Circadian rhythms have a profound effect on our mental and physical health. Indeed, mental health and circadian health are tightly entwined, and circadian interventions can improve mood and well-being, even in healthy people.

Recommendations from the International Society of Bipolar Disorders Task Force on Chronobiology and Chronotherapy and the Society for Light Treatment and Biologic Rhythms.

Blue spectrum light can worsen two systems that are already fragile in people with mood disorders: sleep and circadian rhythms. Fortunately, there are simple solutions to correct this problem.

Concerned about daylight savings time? This patient handout offers tips for getting a good night's sleep.
Sleep-related problems are among the most disabling consequences of TBI, with multiple influences: impairment of neuronal plasticity, metabolomic alterations, loss of vascular homeostasis, and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. The authors take a close look.

Circadian components are profound in depressive disorders, such seasonal affective disorder. This article introduces a course to be given at this year’s APA Meeting in Toronto, on melatonin and light treatment.

What's new in sleep medicine? The latest developments in both new and novel approaches to treating sleep disorders.

Melatonin has a role in psychiatric illness and the treatment of circadian rhythm sleep disorders, insomnia, and comorbid depressive disorders.

Sleep changes associated with psychotropic drugs are common enough to justify routinely obtaining a baseline sleep diary before beginning treatment, even when the initial screening for sleep disorders indicates that no further investigation is needed.

This discussion focuses on approaches to improve medication adherence, particularly in reference to helping adolescents remain on recommended psychopharmacological regimens when transitioning from acute to long-term maintenance.

Recently our inpatient psychiatric unit moved into a brand new facility. In the months and weeks preceding “the move,” there was much preparation and nervous energy. We had been preparing our patients and ourselves for this day. “

Can you name an important part of good sleep hygiene? The use of which short-acting sedative-hypnotics to treat sleep disturbances in patients is associated with Alzheimer disease? These questions and more.
In Part 3 of this 3-part series, Dr Dilsaver discusses dichotomization versus a continuum model and concerns that bipolar disorders are over-diagnosed.

Several available agents in addition to methylene blue are being investigated for bipolar disorder and were in a in a recent review.

Autism is demanding increased attention by professional and lay audiences; prevalence seems to be increasing. There are differing opinions about whether the increase is due to greater recognition and reporting, diagnostic expansion and substitution, or increasing acceptability.
Available treatments are so robust that nearly one-third of patients with major depression will achieve full clinical remission with monotherapy.

What do we know about circadian rhythms and melatonin? And what further lessons do we need about circadian rhythms, light exposure, and melatonin to help our patients with disturbed sleep/wake cycles?

Restless legs syndrome (RLS) is a neurosensory disorder first described by Sir Thomas Willis in 1672. As early as the 19th century, Theodor Wittmaack observed the comorbidity of RLS with depression and anxiety. He termed this condition “anxietas tibiarum” and believed it to be a form of hysteria.

Agitation in older adults is frequently associated with multiple psychiatric and medical conditions and comorbidities. It commonly occurs in patients with anxiety, affective illness, psychosis, dementia, stroke, brain injury, delirium, or pain.

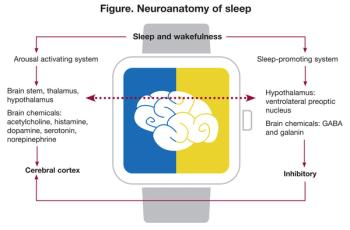
A variety of conditions may account for the sleep difficulties experienced by many older adults, including specific sleep disorders, circadian rhythm disturbances, and medical and psychiatric comorbidities.

Many recall the phrase "To know syphilis is to know medicine." Now Lyme disease (Lyme borreliosis), the new "great imitator," is the ultimate challenge to the breadth and depth of our knowledge. In psychiatry, we generally treat mental symptoms or syndromes rather than the underlying cause of a disorder.

Major depressive disorder (MDD) affects a large proportion of the world's population, but much still needs to be done to categorically improve the lives of people with this condition.

The Science of Sleep. A quirky Indy motion picture by that title was in theaters last year. The plot concerned an odd but wildly creative and endearing fellow who ran into problems in his interpersonal relationships, in part, because he often couldn't distinguish between being awake and asleep. Wake and dream episodes mirrored each other, creating a penchant for the surreal and a personal narrative for the protagonist that wasn't quite in sync with that of the characters around him.

Patients who experience seizure 24 hours after stroke onset may be at increased risk for death, according to Angela Rackley, MD, a clinical neurophysiology fellow in epilepsy, and coresearchers at the University of Cincinnati. Rackley presented an abstract on the incidence of seizures within 24 hours after acute stroke at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society in San Diego this past December. She and colleagues found a higher 30- day mortality rate among patients who had a seizure within hours of stroke compared with patients who did not experience poststroke seizure.